
Newsroom
A research team from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has developed an engineered Escherichia coli strain capable of efficiently producing L-fucose, achieving a substantial increase in yield.
The research findings have been published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry.
L-fucose is a rare monosaccharide known for its numerous health benefits, including promoting gut health, reducing lipid levels, supporting cancer prevention, and enhancing skin hydration. However, traditional production methods have been limited by high costs and low yields, which have hindered its industrial-scale application.
In this study, the researchers systematically optimized the metabolic pathways of Escherichia coli through metabolic engineering. They first screened and integrated key enzyme genes, including α-1, 2-fucosyltransferase and α-L-fucosidase, to direct the metabolic flux towards L-fucose synthesis. By optimizing the gene copy number, they significantly enhanced enzyme expression levels, thereby increasing L-fucose production.
Additionally, they also focused on enhancing the supply of guanosine triphosphate (GTP) and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and optimized metabolic regulation. Additionally, they engineered the 2'-fucosyllactose transporter to reduce the accumulation of 2'-fucosyllactose, further improving the overall production efficiency of L-fucose.
In terms of fermentation strategy, the team adopted a co-fermentation method using glucose and glycerol, optimizing carbon source allocation and improving strain fermentation efficiency. This strategy not only improved nutrient utilization but also led to the highest-ever reported L-fucose titer of 91.90 g/L in a 5-liter bioreactor. This result represents an 80.01% increase over previous records, with a productivity rate of 1.18 g/L·h.
This study not only provides a new technological route for the industrial production of L-fucose but also offers valuable experience and strategies for the field of microbial metabolic engineering.
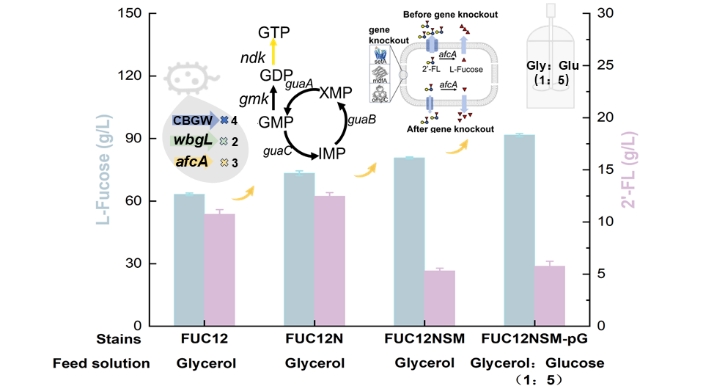
Schematic Diagram of L-Fucose Biosynthetic Pathway Optimization and Fermentation Performance Enhancement (Image by XIA Zihan)
